How do you secure and protect your data in the cloud?
What is cloud security?
Cloud security refers to cloud security policies, security controls and audits. But also, it refers to other solutions that protect data, applications, APIs and your entire cloud infrastructure from the risks associated with security breaches.
Cloud and security breaches
Cloud computing is experiencing increasing popularity and mass adoption. This is being witnessed due to its many advantages such as scalability, affordability, etc… However, there are many potential threats that can arise due to the cloud.
DDDoS attacks
Volumetric DDDoS attacks continue to be prevalent. There is an increase in the size of the attacks and the level of sophistication of the attackers. This occurs when attackers send a large stream of malicious traffic to an application or API. They completely overwhelm its bandwidth capabilities and thus block critical services for its users. This has a huge impact on the company’s bottom line. So you need advanced DDoS detection and protection technology to reduce the impact of these attacks on your network, digital assets, business and customers.
Application layer attacks
Application layer attacks can also cause a lot of damage. As the name suggests, traffic attacks target the application layer, or Layer 7 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. They take over your cloud environment and immitrate user behavior. The targeted applications may be ones you have deployed in the cloud or applications provided by a third-party vendor. As a result, the traffic appears legitimate and becomes difficult to detect. When combined, DDoS and application layer attacks can compromise your entire infrastructure. You need a cloud provider with robust DDoS attack detection to help mitigate these security risks.
How to secure and protect the cloud
Security for private, public and hybrid clouds
Even though public clouds offer more flexibility, many organizations prefer a private cloud environment over public clouds or a hybrid cloud infrastructure. However, the private cloud comes with its own risks. For example, an attacker could exploit a vulnerability, gain access to the hypervisor, the overall system and attack neighboring virtual machines installed on the host server. Those with a public cloud are also exposed to the same vulnerabilities in their infrastructure. However, Amazon, Microsoft or Google offer a faster response to mitigate these risks and are better equipped to ensure your hypervisors’ IT security.
Security breaches and securing data in the cloud
Users must log in to access resources that are in the cloud. To do this, the user must authenticate and be authorized. An attacker could manipulate the registration details. This would give him unwanted access to the cloud infrastructure. You need to make sure that your system does not fall into the wrong hands. In order to avoid such problems, when it comes to security, you need to implement good security practices like an identity and access management (IAM) system. Indeed, it offers features such as web single sign-on (web SSO). However, a misconfigured IAM can lead to an unauthorized user (malicious user or misconfiguration) instantiating prohibited resources. This could further lead to unintended infrastructure costs and instances of fraud, due to breaches, throughout the infrastructure.
Role management is prone to errors, new attack surfaces and can be time consuming. This is why an IAM is important when configuring your applications, to give users precise rights to access only what they really need (parts of the network, storage location, etc.). This approach could be further enhanced by defining some rules based on these roles.
Unforeseen incidents
Serverless applications are recommended for security to automate repetitive tasks and improve overall productivity. It allows code to be written and executed automatically, without having to worry about managing virtual machines or containers, scalability, etc. For example, AWS hosts developers’ code, creates virtual machines and scales them automatically, so you don’t have to manage the entire infrastructure and can focus on your other business priorities. This is truly the next generation cloud. However, it can be expensive to run applications with a serverless architecture.
Let’s say a customer wants to upload their profile picture to your website. Once the image is uploaded, the serverless routine automatically resizes it. In such a scenario, instead of a classic DDoS attack, the attacker tends to create hundreds of fake accounts, changing the profile picture of each account, several times a second. If this costs you at least a few cents for each execution, then you can realize how quickly the total costs would increase. To give an idea, if you pay 100 euros per month for classic traffic and the attack costs you 100 euros, the total costs could reach 10,000 euros per month.
Compliance does not mean cloud security
There are strict regulatory compliance requirements on data. And this must be taken into account by cloud service providers. Since cloud computing caters to many industries, it’s important to have compliance programs in place. Or security practices, to address the various security risks it imposes on consumers. Cloud providers must comply with the protection standards set by HIPAA. But also the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Payment Card Industry (PCI DSS) standard in order to provide customers with the protection they deserve.
Compliance with the GDPR, according to the Schrems II ruling, is necessary to avoid high penalties. These penalties are equivalent to 4% of the company’s global turnover. It is advisable to use a cloud service provider based in the EU, and not affected by foreign laws. This is to ensure that your data in the cloud is protected. After all, you alone will be responsible for this decision. However, attackers can also have a negative impact on compliance programs. The need for security practices and standards in cloud security management continues to grow.
Solutions to secure applications hosted in the cloud
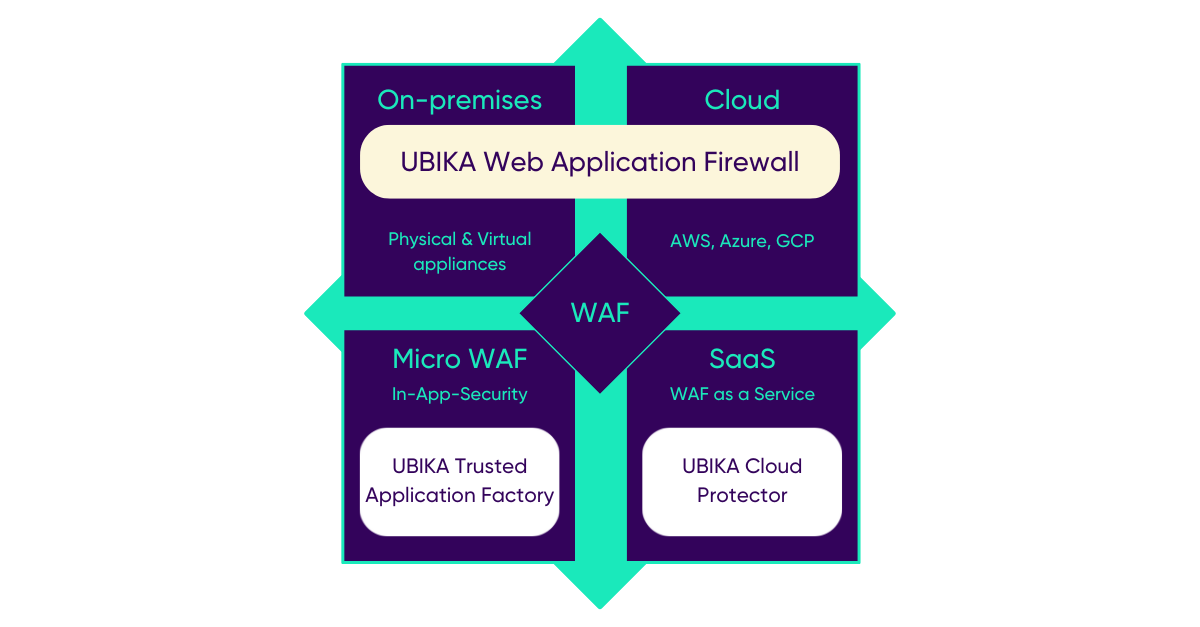
UBIKA addresses the various challenges associated with cloud-specific security. Here are some additional benefits.
UBIKA WAAP Gateway (on-premises/on-premises)
- It enables centralized log management and reporting directly in a SaaS platform – ideal for companies that prefer on-premises management for compliance or security reasons
- Reverse proxy-based web applications and API security controls
- Graphic security policy design and inbound and outbound traffic management
- Total cost of ownership (TCO) optimization in the build and run phases as well as DevOps oriented
- Adaptive approach based on behavioral analysis and IP reputation
- Advanced security, performance and web workload monitoring
UBIKA WAAP Cloud (hosted in the cloud)
Our WAF can also be deployed in the cloud marketplaces. It is very easy to set up and instantiate and has all the benefits of the on-premises version.
UBIKA Cloud Protector (WAF-as-a-Service)
It is ideal for companies that want to rely entirely on Software-as-a-Service deployment in the cloud to be as flexible as possible. Unlike the cloud-hosted version, you don’t have to manage software updates for this one.
- UBIKA WAAP’s security engines are integrated into a WAF-as-a-Service
- Better balance between high-level security and ease of use with predefined policies
- High availability and performance of applications
- Usage-based subscription with vendor managed service
- A trusted and sovereign European solution